SAP HANA
SAP was founded in 1972 as a business applications company but really came into prominence in the 1990s with the ERP boom. Its ERP solution (R/3) was first released in 1992. The vendor employs more than 100,000 people worldwide and had revenues of $30.87 billion in 2022. Today, SAP is one of the largest business software vendors in the world.
SAP’s original strategy was to view BI as an extension of its all-inclusive ERP offerings. In 1998, it launched SAP Business Warehouse (BW), a completely packaged, plug-and-play BI solution designed to complement SAP ERP applications. SAP HANA was launched in 2010 as an in-memory database and ‘application development platform for the processing of high-volume data in real time’. Originally, SAP HANA was available as an appliance only. It has since evolved over many iterations into a universal data platform that is the data back end for almost all SAP business applications. SAP HANA leverages all the advantages that an in-memory approach can offer.
SAP HANA is often connected to an SAP system (called ‘SAP HANA Sidecar Setup’) and runs in parallel to a source SAP ERP application, enabling analysts to access real-time operational and transactional data for analytical processing. It is also the default (and recommended) back end for SAP BW, SAP’s business intelligence and data warehouse platform, now known as SAP BW/4HANA.
Currently, SAP is ploughing much of its data and analytics investment into the cloud, offering a combination of SAP Analytics Cloud as the user tool layer and SAP Datasphere based on SAP HANA Cloud or SAP HANA Cloud itself as the data management layer. This solution portfolio is SAP’s strategic data and analytics offering for the future.

User & Use Cases
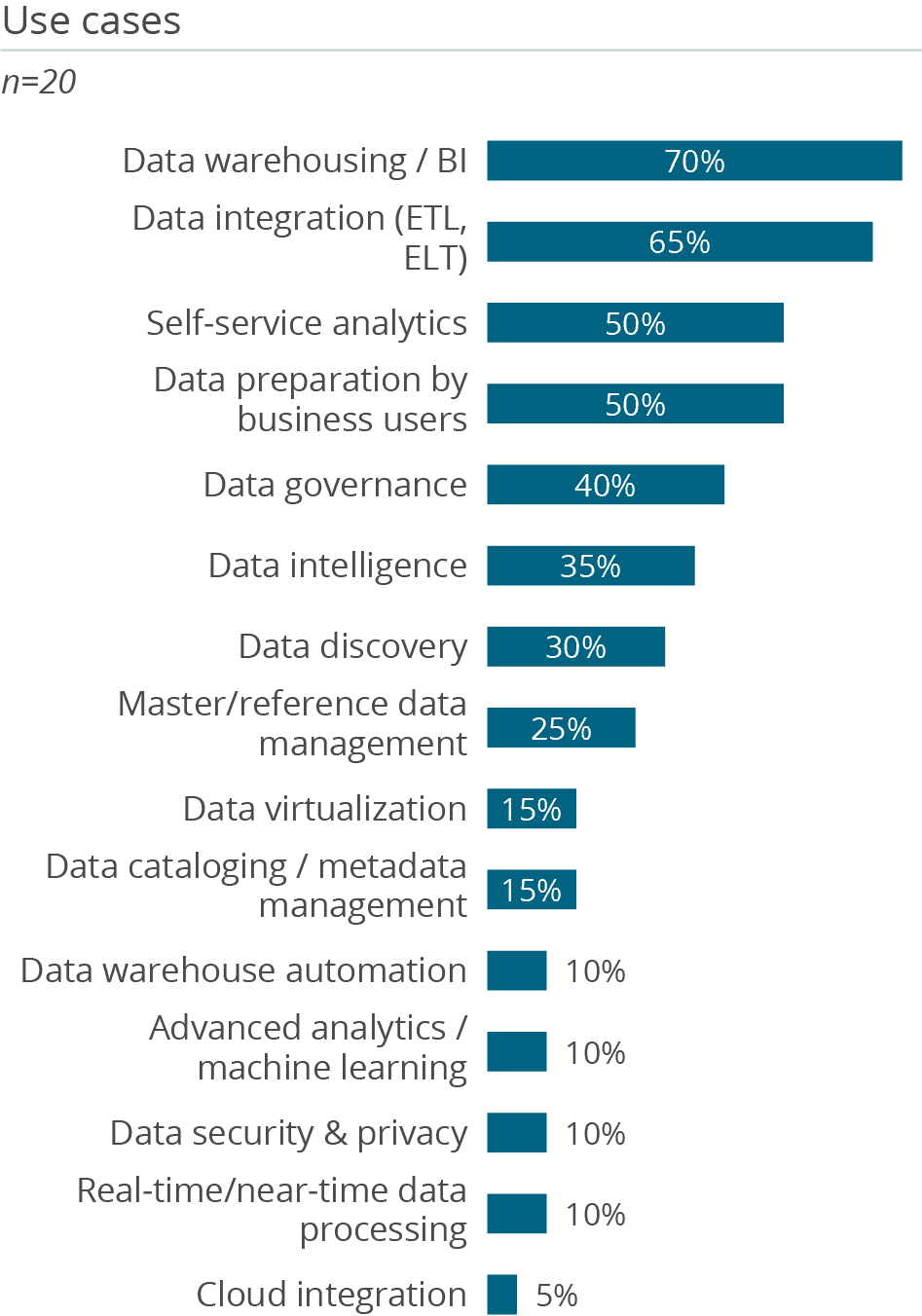
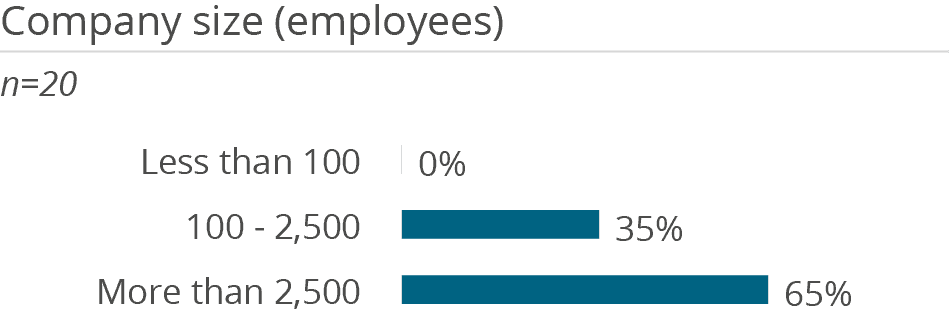
Among respondents to this survey, SAP HANA in mainly used for BI and data warehousing as well as supporting self-service analytics and data preparation. It is notable that only 10 percent are using SAP HANA in real-time scenarios. 80 percent of users have implemented the database on premises while only 5 percent are using HANA as a service on SAP’s own infrastructure, and another 10 percent as a platform as a service on a hyperscaler platform such as Google, Microsoft or Amazon.
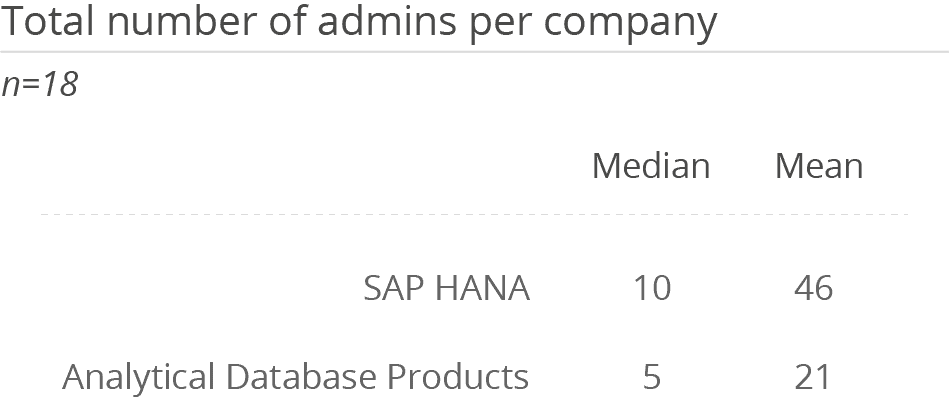
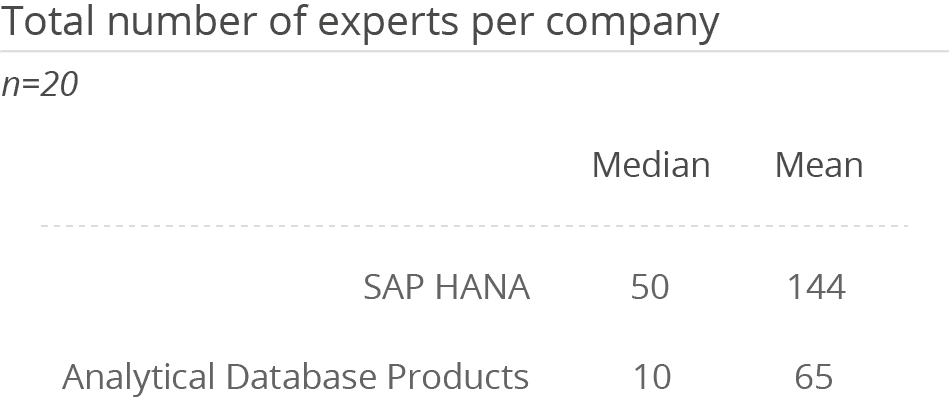
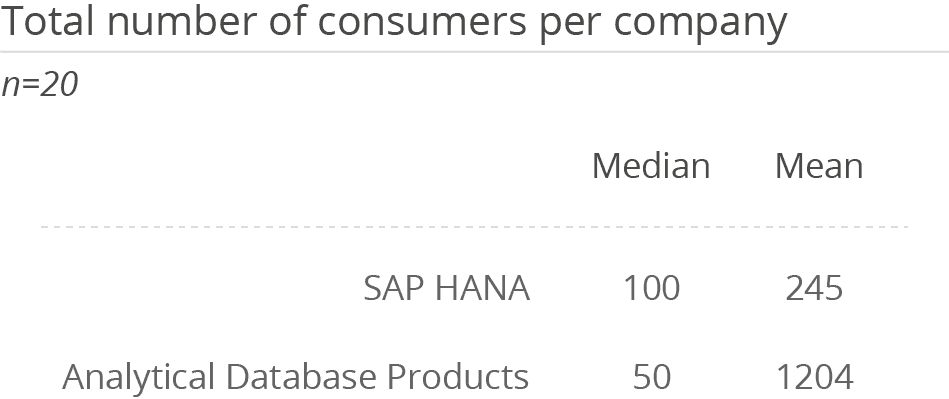
The platform is used by a mean average of 245 users, which is much lower than the overall average of 1,204 for Analytical Database Products. In contrast, the database is predominantly implemented by larger companies. This all leads to the assumption that SAP HANA is likely used in conjunction with SAP BW/4HANA. While SAP BW/4HANA meets most common BI requirements, HANA is used to support self-service scenarios (e.g., by providing SQL access to data directly) or to offer the opportunity to mix up SAP data with non-SAP data.
Want to see the whole picture?
BARC’s Vendor Performance Summary contains an overview of The Data Management Survey results based on feedback from SAP HANA users, accompanied by expert analyst commentary.
Contact us to purchase the Vendor Performance Summary- Register for a free sample Vendor Performance Summary download
- If you have any questions, feel free to contact us
