SAP Datasphere
SAP was founded in 1972 as a business applications company but really came into prominence in the 1990s with the ERP boom. Its ERP solution (R/3) was first released in 1992. The vendor employs more than 100,000 people worldwide and had revenues of $30.87 billion in 2022. Today, SAP is one of the largest business software vendors in the world.
For many years, SAP Business Warehouse (BW) was its strategic offering and foundation for building business intelligence applications. BW is a package consisting of connectors, relational data storage, subject-oriented multidimensional structured data marts and predefined content as well as tools for reporting, analysis and planning, providing a plug-and-play BI solution. However, BW is considered technically complex and has weaknesses in terms of connectivity and its support of self-service analytics for business users. SAP Data Warehouse Cloud was launched in November 2019 as SAP’s new offering for data warehousing in the public cloud to specifically addresses these points. With its rebranding to SAP Datasphere in March 2023, SAP announced a new generation with improvements especially in the areas of data sharing and collaboration as well as in the sense of an open data ecosystem for the im-plementation of a business data fabric. The aim of the product is to provide a unified experience for data integration, data cataloging, semantic modeling and data virtualization – as well as data ware-housing – which makes SAP Datasphere the strategic successor of SAP BW and SAP BW/4HANA.
While providing a flexible, cloud-based option for the enterprise data warehouse, the solution is also designed to empower line-of-business users to perform self-service analytics by means of a business semantic layer. It follows a federate-first approach to reduce or completely avoid upfront data move-ment. This increases agility and reduces the required data management footprint. It can be deployed as a standalone solution or to complement existing SAP or non-SAP data warehouses on-premises or in the cloud. It supports a wide range of connectivity to SAP and non-SAP data sources. SAP Datas-phere data objects are exposed as tables and views. This makes it possible for external data pipelines and analytics tools to utilize them as target or source respectively. The solution offers a governed sandbox concept for combining enterprise data sources with individual and external data in a domain or use-case-specific area called Spaces. If required, sandbox results can be transferred as seamlessly as possible into the enterprise environment.
SAP Datasphere is one of the four fundamental pillars of SAP’s data and analytics strategy. Together with SAP Master Data Governance, it forms the backbone of data management. Further pillars are SAP HANA Cloud as the underlying database and SAP Analytics Cloud for analytics and planning. SAP BW/4HANA will be supported until at least 2040. The general recommendation for SAP BW customers is to move to SAP Datasphere. SAP BW Bridge is an SAP Datasphere feature that provides a transition path to the public cloud and enables existing SAP BW customers to move existing data models to the strategic target solution SAP Datasphere.

User & Use Cases
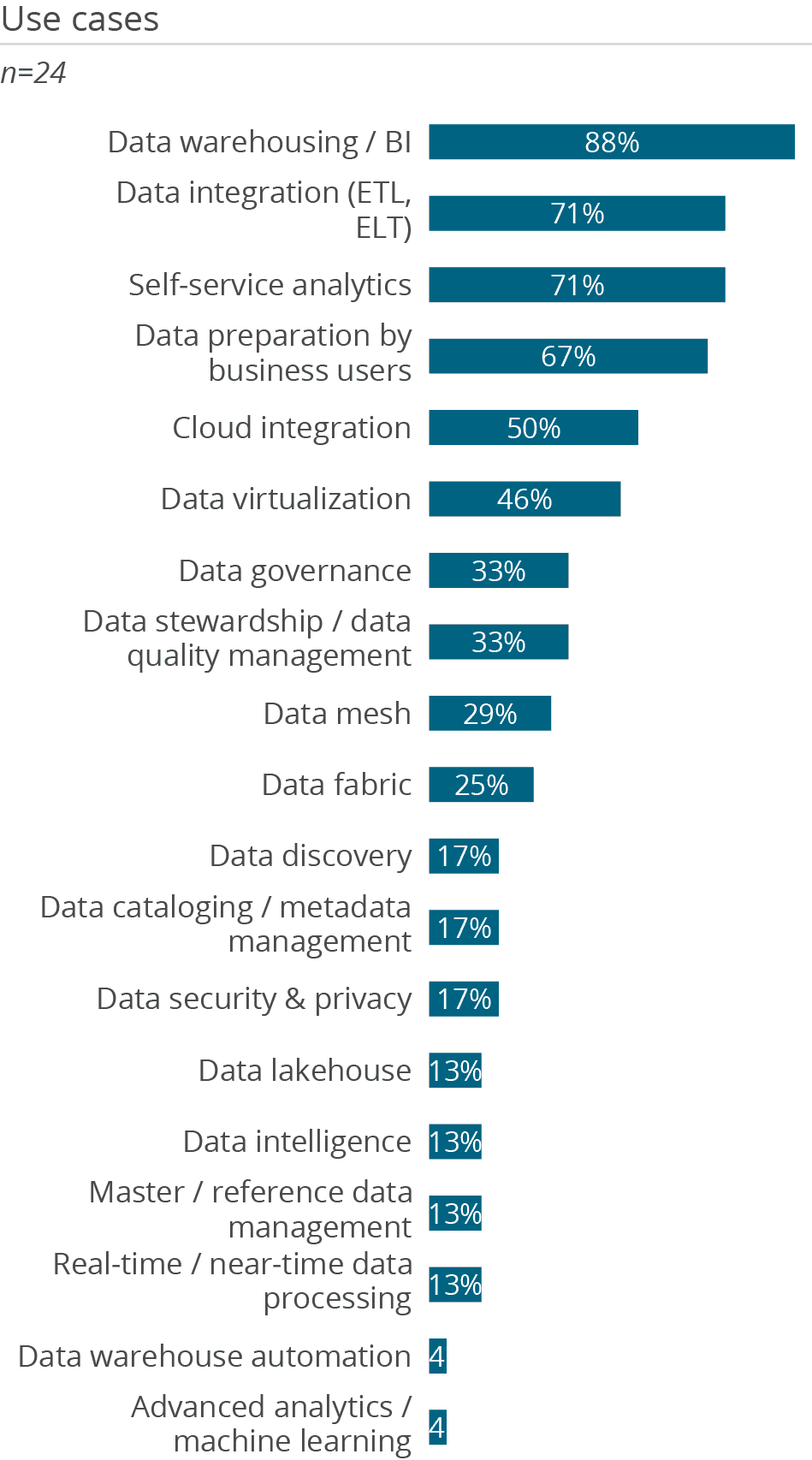
It is not surprising that most users (88 percent) leverage SAP Datasphere Warehouse Cloud as a data warehouse. A large proportion of users (71 percent) use the platform for self-service analytics. This is to be expected, since the predecessor version SAP Data Warehouse Cloud was primarily targeted at this use case. It seems these scenarios have even increased, as the figure has grown since last year (52 percent). 67 percent also use SAP Datasphere for data preparation by business users. This is only slightly behind the rate of use for data integration (71 percent).
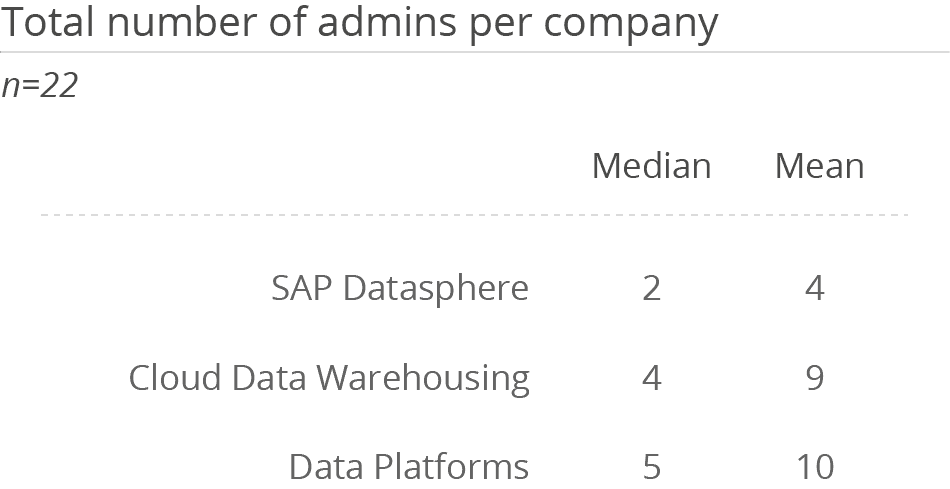
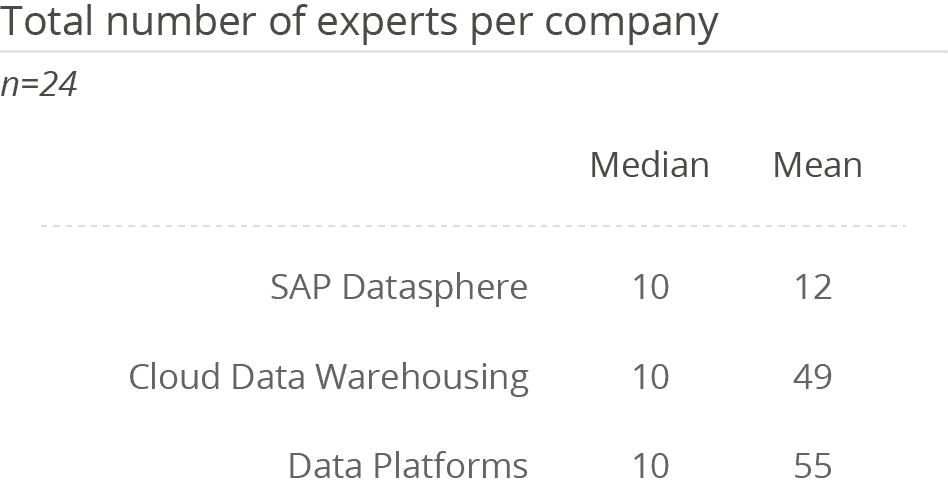
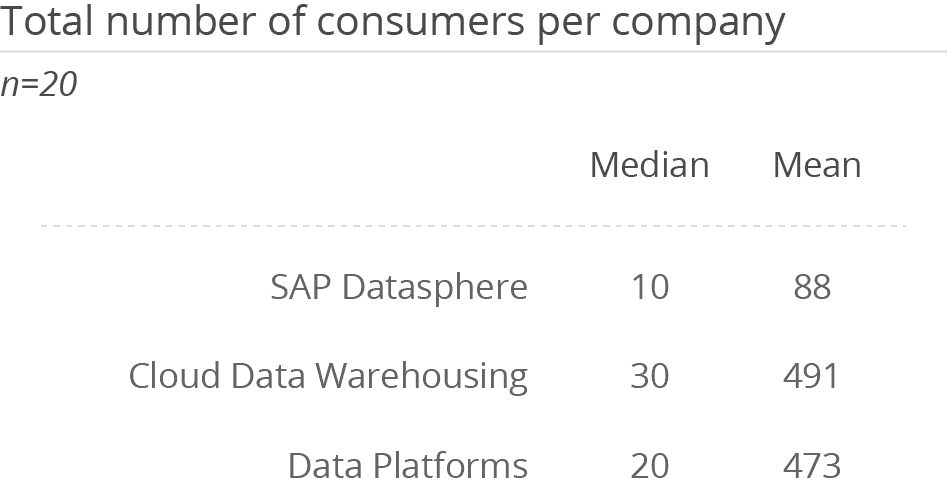
Utilization of SAP Datasphere for data governance and data stewardship/data quality management (both 33 percent) has grown impressively compared to last year (9 and 3 percent respectively). This may indicate that the functions the product provides (such as the Spaces concept) to support these areas are being utilized in practice more often than in the past. The increased utilization of the solution in these areas is consistent with the increase in number of users compared to last year. Although the number of admins, experts and users is lower than the overall figures for the Cloud Data Warehousing and Data Platforms peer groups, these numbers are higher than in last year’s survey. This may be at-tributed to the fact that no companies with less than 100 employees evaluated SAP Datasphere in this year’s survey.
SAP Datasphere is most frequently deployed as a software as a service (79 percent). With this cloud offering, SAP appears to be successful at encapsulating administrative overhead for operating a data landscape. Both the median and mean number of admins is lower than average in the Cloud Data Warehousing and Data Platforms peer groups.
Want to see the whole picture?
BARC’s Vendor Performance Summary contains an overview of The Data Management Survey results based on feedback from SAP Datasphere users, accompanied by expert analyst commentary.
Contact us to purchase the Vendor Performance Summary- Register for a free sample Vendor Performance Summary download
- If you have any questions, feel free to contact us
