SAP BW/4HANA
SAP was founded in 1972 as a business applications company but really came into prominence in the 1990s with the ERP boom. Its ERP solution (R/3) was first released in 1992. The vendor employs more than 100,000 people worldwide and had revenues of $30.87 billion in 2022. Today, SAP is one of the largest business software vendors in the world.
SAP’s original strategy was to view BI as an extension of its all-inclusive ERP offerings. In 1998, it launched SAP Business Warehouse (BW), a completely packaged, plug-and-play BI solution designed to complement SAP ERP applications. BW is a package consisting of connectors, relational data storage, subject-oriented multidimensional structured data marts and predefined content as well as tools for reporting, analysis and planning. The goal was to provide a plug-and-play BI solution that would make it fast and easy for SAP customers to benefit from BI.
There are different versions of BW available. Traditional BW runs on third-party databases such as Mi-crosoft SQL Server and Oracle for data storage. The “powered by SAP HANA” version uses SAP’s own HANA platform. SAP BW/4HANA will only run on SAP HANA. It uses different modeling objects with modeling taking place in HANA Studio (SAP HANA’s development environment) instead of the SAP GUI (the BW development environment) and leverages additional tools based on HANA technology (e.g., for data integration).
With BW/4HANA, SAP released its next-generation data warehousing offering in 2016. The overall con-cept and goal of this package remains similar to the approach with BW: to provide software support for customers to integrate SAP operational data sources with other data sources and create a data warehouse which exposes its data to different front ends. In contrast to BW, the new BW/4HANA solu-tion does not include front-end tools anymore. The following document refers to SAP BW/4HANA.
SAP BW/4HANA is a completely revamped version of SAP BW that runs on the SAP HANA in-memory database. The new product improves performance and scalability, simplifies development and opera-tion, and supports a variety of in-database analytic functions. It is mainly designed to support multiple analytic use cases, ranging from standard reporting and dashboarding to dimensional analysis. Basic support for real-time and advanced analytics is also included. Although it is not without challenges, the platform supports an array of functionality:
- Data integration to combine data from varied sources and data types.
- Real-time access to or replication of sources based on HANA’s in-memory architecture.
- Algorithm push-down of operations/calculations to HANA supporting query calculations, plan-ning functions and transformation logic.
- HANA foundation-based spatial and graph support as well as text and predictive analytics.
- Data Tiering Optimization (DTO) for managing hot, warm and cold data.
In on-premises analytics environments, the HANA database is often considered both natively and within SAP BW/4HANA. Currently, SAP is ploughing much of its data and analytics investment into the cloud, offering a combination of SAP Analytics Cloud as the user tool layer and SAP Datasphere based on SAP HANA Cloud as the data management layer. This solution portfolio is SAP’s strategic data and analytics offering for the future. The general recommendation for SAP BW customers is to move to SAP Datas-phere. There are several paths possible, depending on many factors including the situation of the cus-tomer, the state of the source system, and the business requirements.

User & Use Cases
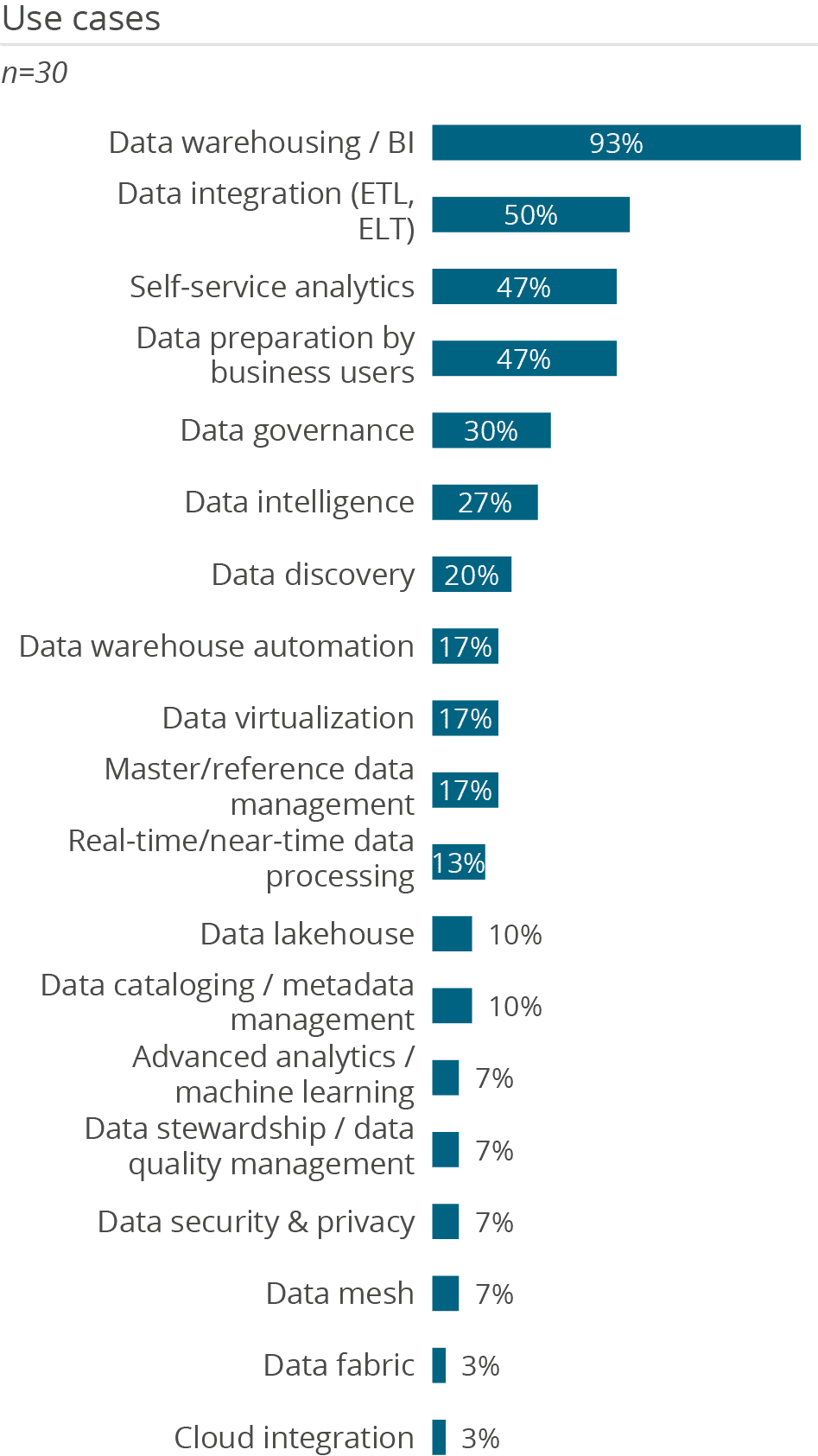
It is not surprising that 93 percent of users leverage SAP BW/4HANA as a data warehouse. A large proportion (50 percent) also use it for data integration, although this figure has dropped since last year (67 percent). These are the use cases SAP BW typically supports. Surprisingly, 47 percent of survey participants claim to utilize SAP BW/4HANA as a tool for data preparation for business users. In our view, data preparation as an iterative process in which business users prepare almost code-free data sets for exploration is not what is meant here. It is more likely they are referring to data preparation (data integration) for data warehousing. It is worth mentioning that there has been an increase in use for self-service-analytics (47 percent) and data discovery (20 percent) compared to last year (40 and 16 percent respectively). This could be a result of the increasing adoption of SAP Analytics Cloud, which has a native connection to BW and provides good user support for these use cases. This trend also explains the increased use of BW for data governance (30 percent versus 20 percent). By contrast, only 17 percent use BW for data virtualization. This is a significant drop from 42 percent the previous year and suggests that customers are not satisfied with BW’s coverage of this area.
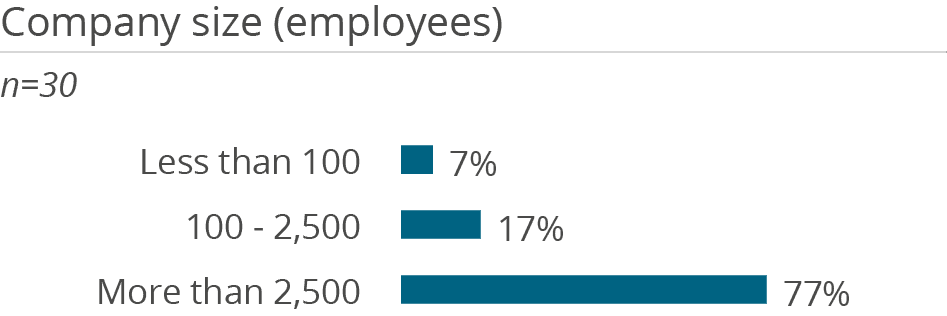
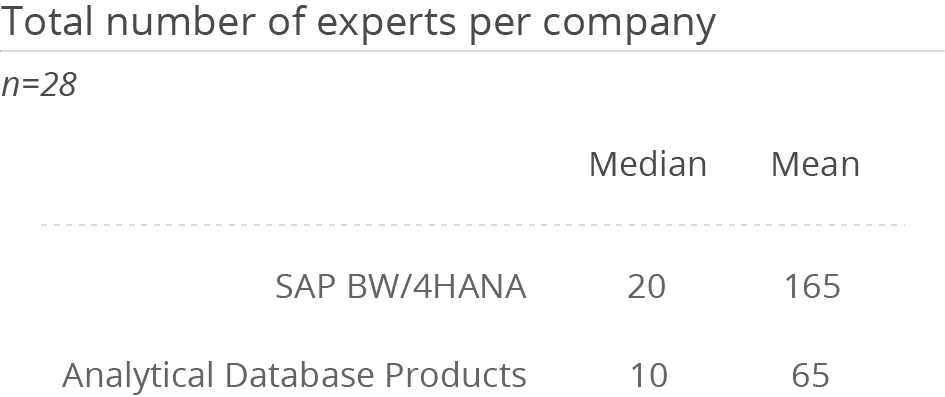
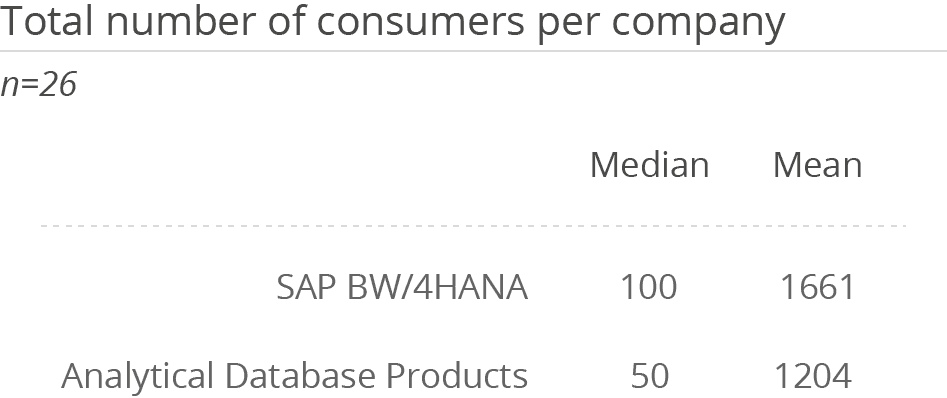
Usage of SAP BW/4HANA is very widespread in companies. Most median and mean numbers of per-sonas working with the solution are above the average figures in the Analytical Database Products peer group. The product is used primarily by large organizations with more than 2,500 employees (77 per-cent).

Want to see the whole picture?
BARC’s Vendor Performance Summary contains an overview of The Data Management Survey results based on feedback from SAP BW/4HANA users, accompanied by expert analyst commentary.
Contact us to purchase the Vendor Performance Summary- Register for a free sample Vendor Performance Summary download
- If you have any questions, feel free to contact us
