PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL, often termed “Postgres”, began in the 1980s at the University of California, Berkeley, evolving from the Ingres project led by Michael Stonebraker. By 1994, Postgres95 introduced SQL support. Renamed to PostgreSQL in 1996 to reflect its enhanced SQL capabilities, it became an open-source object-relational database management system. Over decades, it has grown in features and popularity, emphasizing extensibility, standards compliance and data integrity. Today, it is a top choice for various applications, backed by a vibrant open-source community. With a community-driven approach, it aims to offer a robust, reliable and versatile database solution for a broad spectrum of applications and industries.
It allows users to store, organize and retrieve data, supporting both SQL (relational) and JSON (non-relational) querying. PostgreSQL emphasizes standards compliance, data integrity and supports advanced data types, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from small single-machine apps to large internet-facing applications with many concurrent users.
PostgreSQL is used for web applications, analytics, geospatial databases, data warehousing, enterprise applications, CRM systems, content management, financial applications and scientific research, among others. Its versatility supports both relational and non-relational data models, catering to a broad spectrum of use cases.
The development and enhancement of PostgreSQL is driven by a global community of volunteer developers, contributors and enthusiasts. This decentralized, collaborative approach ensures diverse input and continuous improvement. Key decisions are made by the PostgreSQL Core Team, but the broader community actively contributes to its evolution and refinement.
It is also worth noting that while the core PostgreSQL project has remained free and open-source, its extensibility has led to numerous extensions and commercial forks that provide additional capabilities or cater to niche markets.
The PostgreSQL partner landscape comprises companies offering managed services, consulting and extensions. Key players include cloud providers such as AWS, Google Cloud and Azure with managed PostgreSQL offerings. Specialist firms, such as EnterpriseDB, Citus Data (e.g., adding parallel processing or high availability capabilities) and 2ndQuadrant, provide consultancy, support and tools. Many partners also contribute to PostgreSQL’s development, fostering its growth and adoption. Moreover, the database is used in many professional tools in the data and analytics market.

User & Use Cases
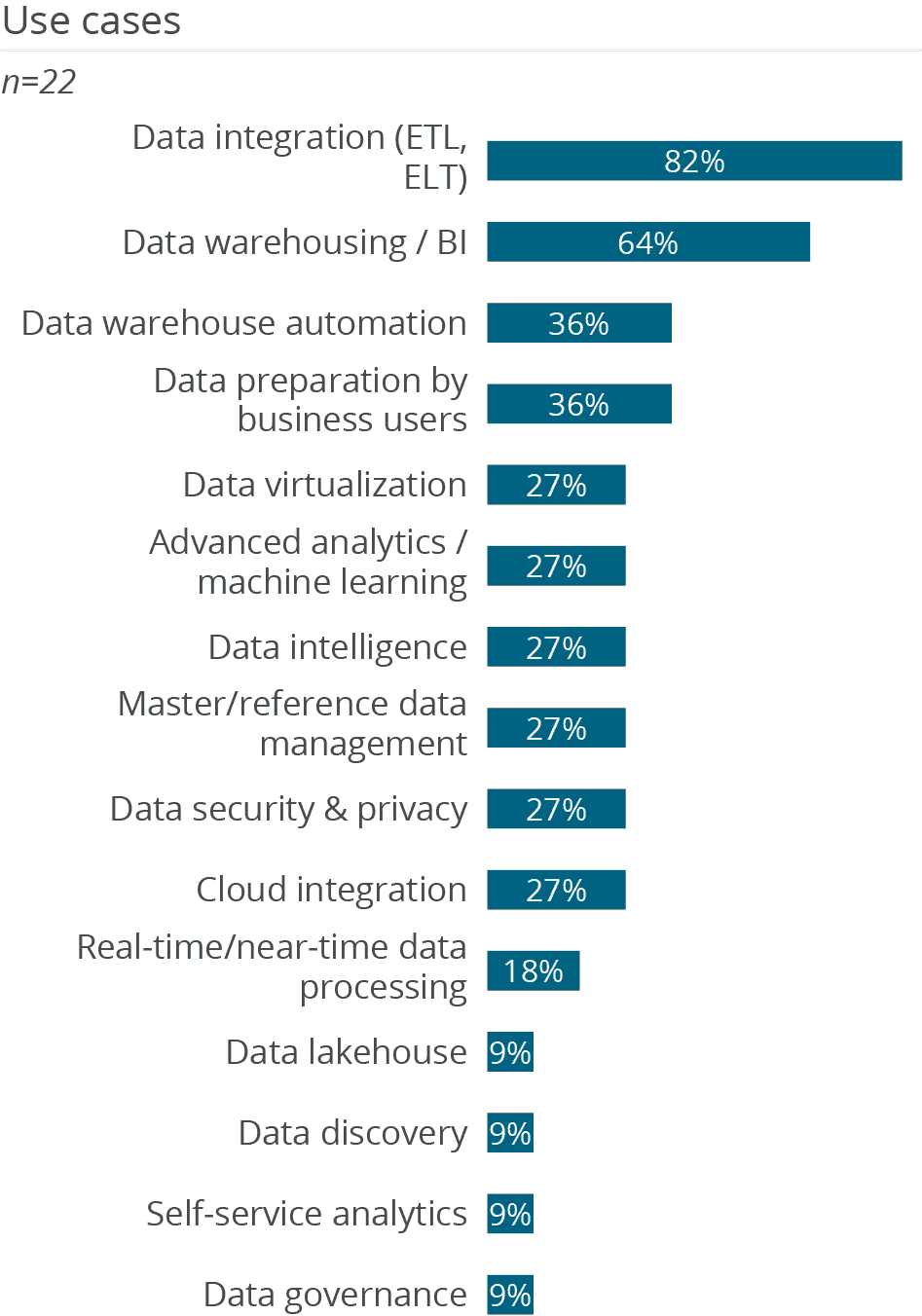
PostgreSQL is a multifunctional database that covers a wide range of dispositive as well as operational use cases. Respondents to this survey mainly use the database for ‘data integration’ and ‘data warehousing / BI’.
The relatively high frequency of ‘data virtualization’ scenarios for this database is interesting. One in three companies seems to use the database to get an integrated, logical view of distributed data.
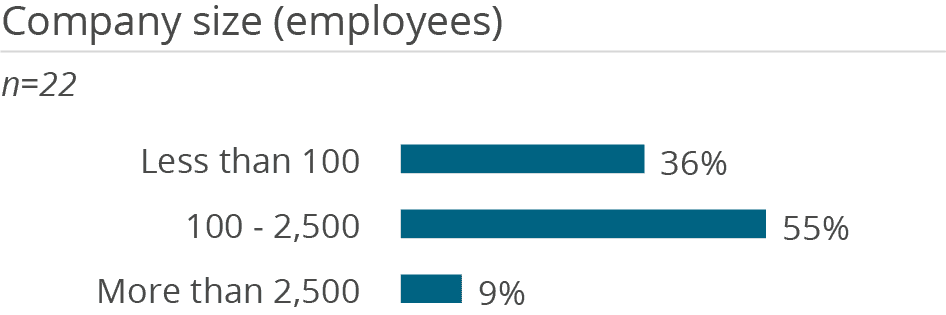
The database is mainly used by companies with 100-2,500 employees or smaller companies. Its typical scenarios are manageable in terms of the number of users, which suggests use in smaller applications. This could also be due to a lack of enterprise features.
The database is usually implemented as a platform as a service on Amazon, Google or Microsoft, on-premises or in hybrid scenarios.

Want to see the whole picture?
BARC’s Vendor Performance Summary contains an overview of The Data Management Survey results based on feedback from PostgreSQL users, accompanied by expert analyst commentary.
Contact us to purchase the Vendor Performance Summary- Register for a free sample Vendor Performance Summary download
- If you have any questions, feel free to contact us
