Amazon Redshift
Amazon was founded in 1994 in Washington State and is now headquartered in Seattle, WA. Originally an online book store, the company is now a broadbased technology provider of e-commerce, cloud computing and streaming services. The company has a variety of subsidiaries including Amazon Web Services, Whole Foods Market and MGM Entertainment. Amazon has become a household name through its online marketplace and more recently its streaming service. However, Amazon Web Services (AWS) also leads the cloud computing industry, accounting for 32 percent of the market and working with more than 90 percent of Fortune 100 organizations.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers 200 services including data storage, computing, and machine learning and artificial intelligence applications. The AWS Marketplace features over 4,000 data products allowing third-party sellers to connect with potential buyers. AWS serves government organizations, large and small enterprises, education institutions and individuals. It has over 1 million active users, 10 percent of those being large scale-organizations. Amazon currently serves 114 Availability Zones (logical network of data centers) in 36 regions around the world.
The services provided are closely integrated with each other. Amazon Redshift is a relational, massively parallel processing data warehouse with columnar storage and OLAP functionality based on PostgreSQL, which integrates seamlessly with Amazon Data Lake based on S3. The service extends the S3 object storage. Amazon Web Services offers its various services as building blocks. Therefore, Amazon Redshift can integrate with other AWS services, including for example its machine learning service Amazon SageMaker, which is now also available directly from within Amazon Redshift through SQL.
Data can be loaded from S3 into Amazon Redshift and prepared, stored and queried in an optimized way for BI/analytics workloads and unloaded back to S3 to be consumed from there. Amazon Redshift Spectrum (a Redshift feature) enables queries on combined data from Redshift and S3 (Data Lake) or direct queries to S3. Queries on file formats such as CSV, Parquet, Avro and JSON are supported, thus avoiding unnecessary data copies or data movement. This is an essential feature in AWS’s quest to build a modern data and analytics architecture that is not only designed for a specific use case but is open, flexible and scalable.
Amazon Redshift RA3 compute instances also include a hardware-based Advanced Query Accelerator, which is designed to provide a significant performance boost of up to 10 times for queries. Advanced data sharing capabilities allow the integration of multiple Amazon Redshift data warehouse instances without the need to copy or move data. This can help to improve reliability through virtual data replication and also supports highly distributed data warehouse or application scenarios.
To load data into Amazon Redshift, users can employ the COPY command or leverage cloud ETL services from AWS itself or one of several third parties from the broader AWS partner landscape.
AWS offers many data and analytics services alongside Amazon Redshift. While functional overlaps exist, each service is tailored to a specific use case. The company believes in closely mapping services to very specific use cases and giving users the flexibility to choose the best service for their needs.
Overall, Amazon Redshift is suitable for classic data warehousing but also complex SQL processing for reporting, business intelligence and advanced analytics purposes.
The latest enhancements to Redshift include faster query performance, more effortless data integration, enhanced security and better cost efficiency.

User & Use Cases
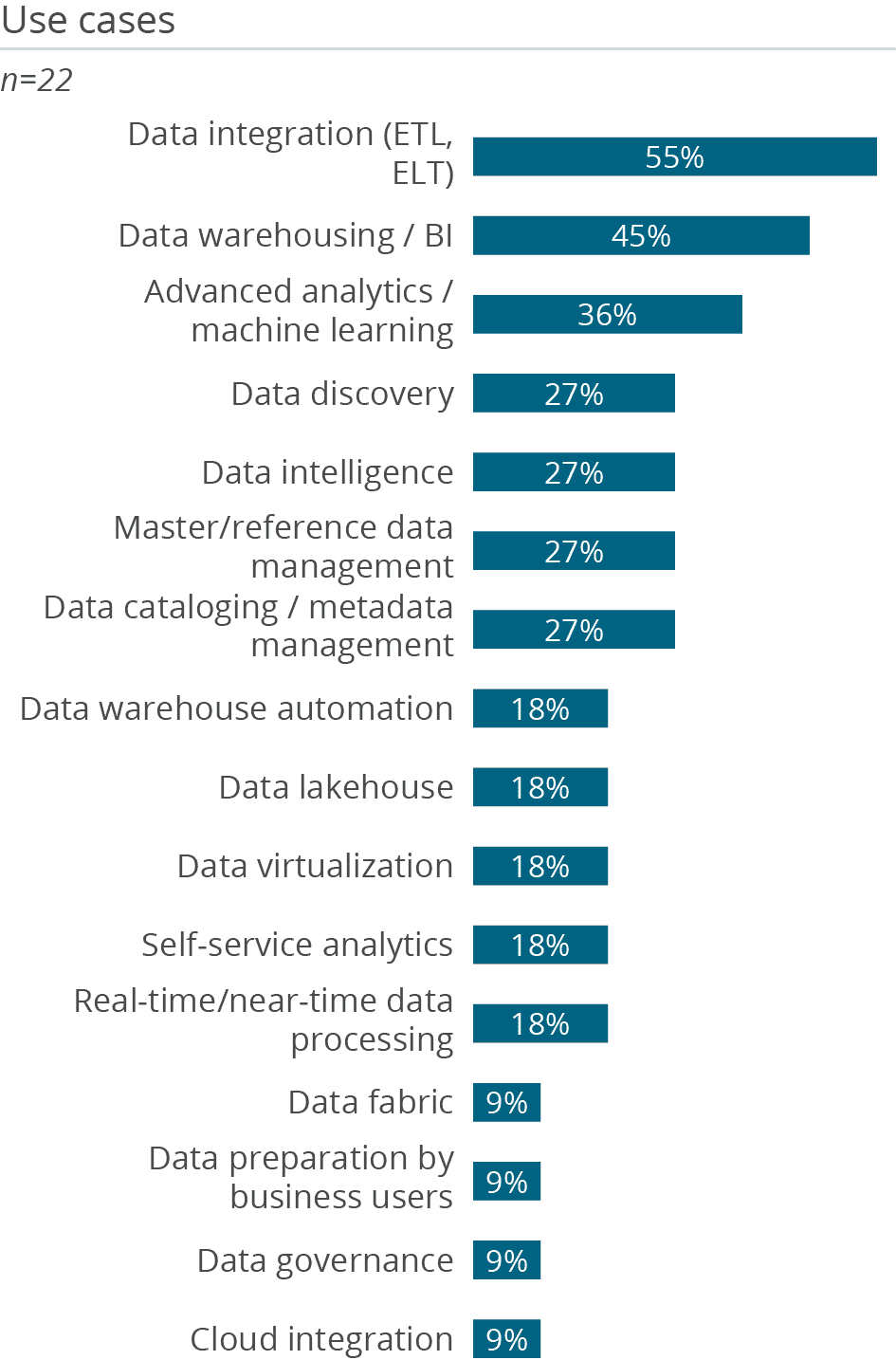
Amazon Redshift features an analytic database with broad functional coverage that enables multiple use cases. It is used for data integration by 55 percent, data warehousing by 45 percent and advanced analytics by 36 percent of customers. Respondents to this survey also reported using it as a data lakehouse (18 percent).
This broad scope of analytical tasks shows that Amazon’s dedicated service for data warehousing has been extended to cover BI and advanced analytics workloads. In contrast, only 33 percent are using Redshift as a data lake so it can be seen as an analytical engine rather than a simple data store, although 56 percent of users stated that they use Amazon as data storage for data provisioning. It is interesting that 27 percent of users claim to do master data management, data cataloging or data discovery. This is surprisingly high as the Amazon Redshift service does not directly cover these areas and requires the utilization of, and integration with, other Amazon services.
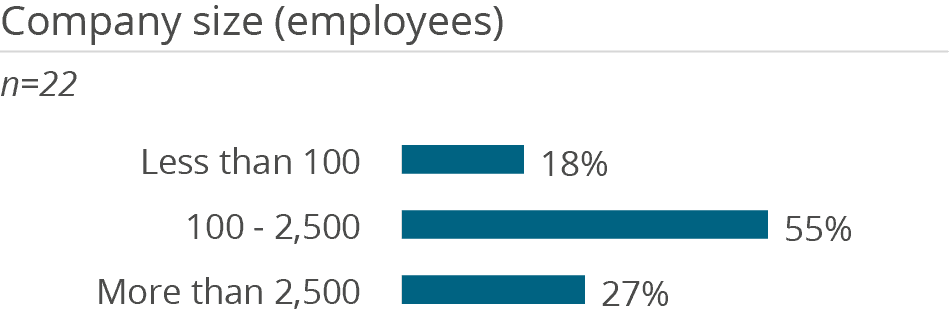
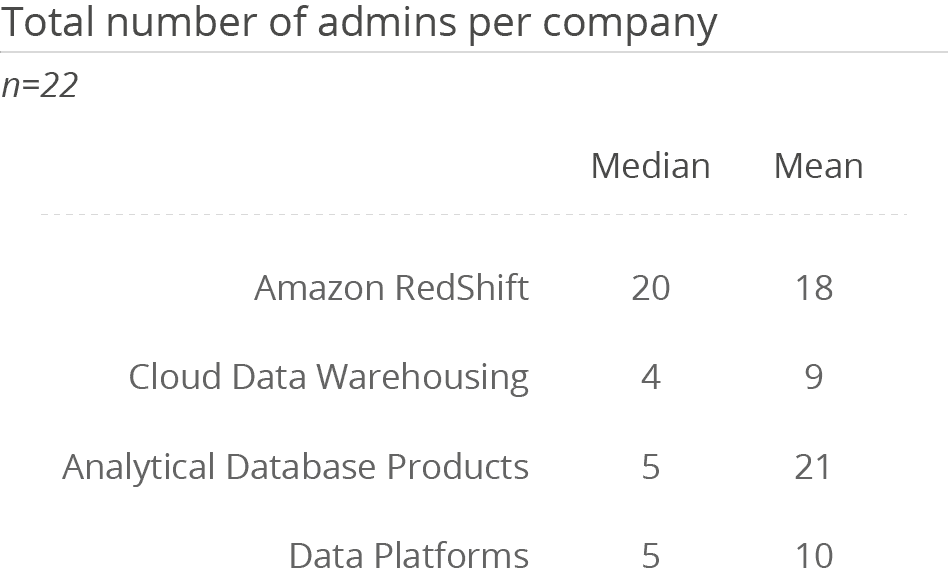
Redshift is mainly used by medium-sized companies (55 percent). A low average number of users indicates small to medium usage scenarios. The tool is mainly used by experts. Here, Amazon Redshift is clearly above the average in its peer groups. The tool therefore seems to be used more as a platform for experts than for widespread use in companies. However, this also fits in with Amazon’s image of offering 200 analytical services. Amazon offers a robust platform for data preparation and provision, with numerous integrated services that can be flexibly combined. Depending on the application, these support experts in building solutions.

Want to see the whole picture?
BARC’s Vendor Performance Summary contains an overview of The Data Management Survey results based on feedback from Amazon Redshift users, accompanied by expert analyst commentary.
Contact us to purchase the Vendor Performance Summary- Register for a free sample Vendor Performance Summary download
- If you have any questions, feel free to contact us
